Overview
Salaried employees may find themselves working less than 40 hours per week, especially if they are classified as non-exempt. This classification means they are entitled to overtime pay for any hours worked beyond that threshold.
Understanding employment classifications is crucial, as it directly impacts your rights and job security. Have you ever felt uncertain about how your hours affect your pay? It’s important to recognize that you are not alone in these feelings.
The implications of reduced hours can weigh heavily on your mind, but knowing your rights empowers you to negotiate for more flexible work arrangements. Together, we can navigate these challenges and ensure that you feel supported in your career journey.
Introduction
In today’s evolving employment landscape, many individuals find themselves in salaried positions, with approximately 60% of employees in the United States engaged in such roles as of 2025. This shift towards fixed salary structures brings a sense of financial stability and job security, yet it can also introduce complexities that may feel overwhelming.
Have you ever wondered about the differences between exempt and non-exempt classifications? Or how reduced work hours might affect your role? Navigating the world of salaried employment requires a keen awareness of labor laws and organizational policies, and we understand that this can be daunting.
As you strive to balance personal aspirations with professional commitments, understanding these dynamics becomes essential for making informed career decisions and achieving financial independence. You are not alone in this journey; many share your concerns and uncertainties. This article delves into the intricacies of salaried employment, offering insights that empower you to take control of your career path. Together, we can explore the challenges and find comforting solutions that resonate with your aspirations.
Understanding Salaried Employment: Definition and Key Characteristics
Salaried positions provide a unique setup where individuals receive a fixed compensation amount, typically disbursed monthly or bi-weekly. Unlike hourly staff, salaried individuals are not compensated based on the time they work, which often leads to important discussions about whether salaried employees can work less than 40 hours per week while still fulfilling their job obligations.
-
Fixed Salary: Workers receive a predetermined salary, ensuring financial stability regardless of hours worked. This stability is crucial for those seeking to mitigate risks and accelerate their job transitions.
-
Job Responsibilities: Salaried individuals are generally tasked with specific duties and performance goals, which may require flexible working hours to meet organizational needs. This flexibility brings up questions about balancing personal aspirations with professional commitments. Recently, there has been a 0.6% increase in real average weekly earnings from February 2024 to February 2025, indicating a positive outlook for salaried workers. Moreover, the total private real average hourly earnings have increased by $0.01, suggesting that the labor market is evolving. Salaried positions are becoming increasingly attractive due to their stability and benefits.
Expert opinions highlight that salaried employment can offer a sense of security and predictability, which is particularly valuable in today’s dynamic job market. Parnell Woodard, an Ownership Coach, emphasizes that transitioning from traditional employment to ownership empowers individuals to achieve their professional goals. Organizations like The Entrepreneur’s Source provide a comprehensive coaching approach, including unique consulting strategies, no-cost coaching services, and a structured process. This underscores the importance of understanding these employment characteristics, empowering individuals to leverage their transferable skills, engage with their communities, and make informed career decisions. You are not alone in navigating these transitions; together, we can work towards creating the lifestyle of your dreams.
Exempt vs. Non-Exempt Salaried Employees: What You Need to Know
Salaried workers face significant challenges under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), as they fall into two primary classifications: exempt and non-exempt. This classification profoundly influences their eligibility for overtime pay and shapes the expectations surrounding their work hours.
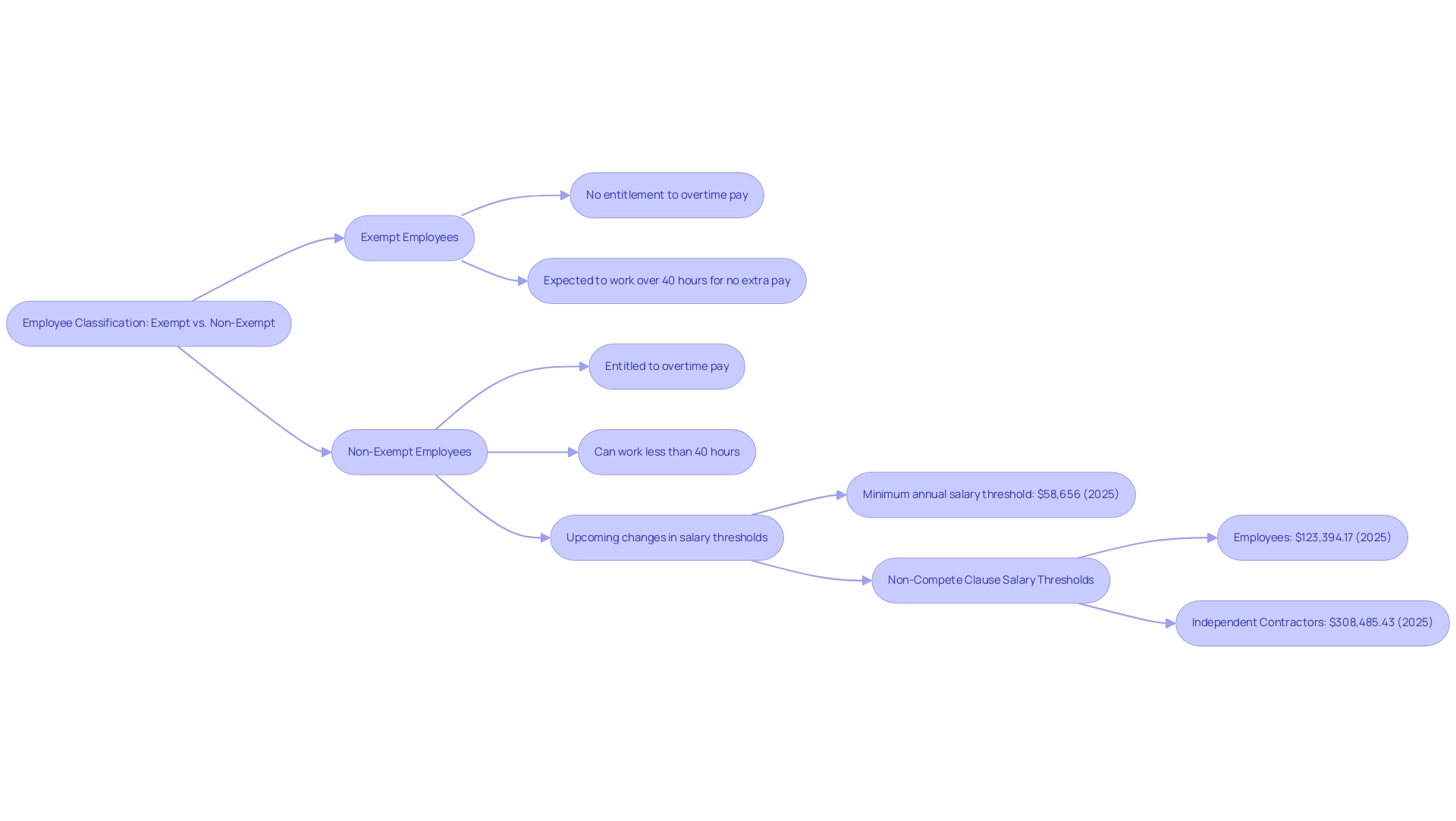
- Exempt Employees are those who are not entitled to overtime pay, typically occupying roles with executive, administrative, or professional responsibilities.
For exempt staff, the expectation is to dedicate the necessary time to fulfill their job responsibilities. This raises a crucial question: can salaried employees work less than 40 hours per week? Often, this role requires exceeding the typical 40-hour workweek without additional compensation. As of 2025, approximately 65% of salaried workers in the U.S. are categorized as exempt, underscoring a trend of increasing demands for work hours without commensurate pay.
- Non-Exempt Workers, on the other hand, can indeed work less than 40 hours per week and are entitled to overtime compensation for any hours worked beyond that threshold. They must receive pay at a minimum rate of 1.5 times their regular pay for these overtime hours. Understanding this distinction is vital for workers to grasp their rights and obligations, particularly with recent updates to the FLSA. For instance, the minimum annual salary threshold for non-exempt status is set to rise to $58,656 on January 1, 2025. This change reflects ongoing adjustments to labor laws designed to protect workers. Furthermore, starting July 1, 2027, salary thresholds will automatically update every three years, indicating a continued evolution in labor regulations.
Recent case studies illustrate the implications of these classifications. For example, the Washington State Department of Labor & Industries has established salary thresholds for non-compete clauses, enforceable only for higher-earning individuals. In 2025, the threshold for workers will be $123,394.17, while independent contractors will see a threshold of $308,485.43. This ensures that non-compete agreements do not unduly restrict lower-income workers, highlighting the importance of understanding one’s classification.
As labor law experts emphasize, the distinction between exempt and non-exempt classifications is not merely a matter of semantics; it directly impacts workers’ financial well-being and job security. Parnell Woodard, a Professional Ownership Coach, notes that transitioning from traditional employment to ownership can empower individuals to navigate these complexities more effectively. By understanding these classifications and their implications, individuals can take proactive steps toward achieving financial freedom and personal agency in a changing job market.
This understanding aligns with the mission of The Entrepreneur’s Source, which offers no-cost coaching services and a structured process to help clients gain clarity and confidence in their career decisions. You are not alone in this journey; support is available to help you navigate these complexities.
Navigating Labor Laws: The Fair Labor Standards Act and Its Implications
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) is pivotal in defining the rights of salaried workers, particularly regarding minimum wage, overtime pay, and recordkeeping standards. Understanding these implications is essential for navigating the complexities of employment in South Carolina, especially with the anticipated changes in 2025.
-
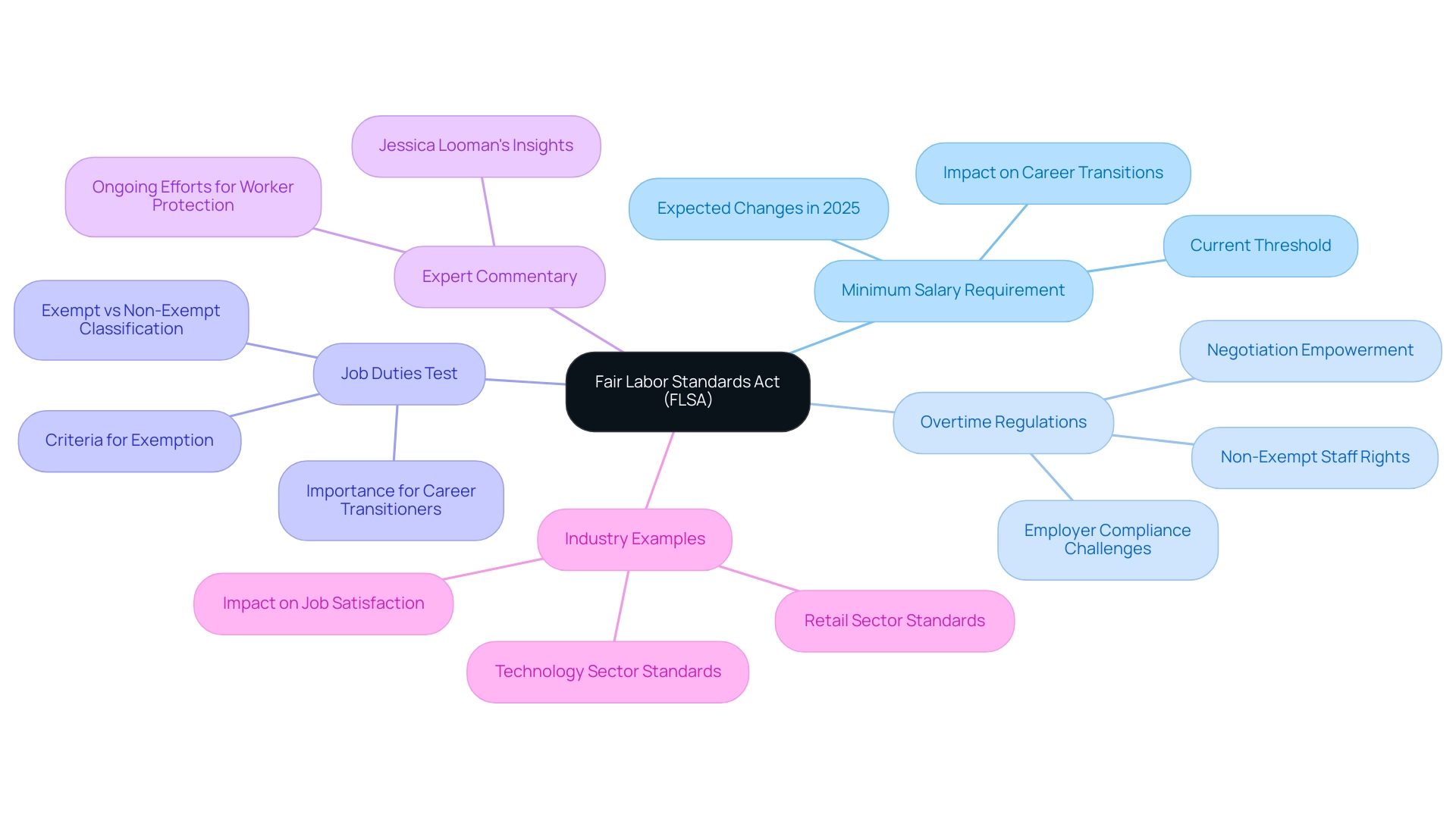
Minimum Salary Requirement: As we approach 2025, the minimum salary requirement for exempt staff is expected to rise, reflecting ongoing adjustments aimed at ensuring fair compensation. Currently, this threshold stands at $684 per week, but regular updates are critical to prevent the erosion of overtime protections over time. This is particularly relevant for those in career transitions who may be evaluating their options and seeking roles that meet these updated standards, thereby enhancing their employability and financial freedom.
-
Overtime Regulations: Non-exempt salaried staff can indeed work less than 40 hours per week, as they are entitled to extra compensation for any time worked beyond that threshold. Employers must diligently track the hours worked by these individuals to comply with FLSA regulations. This is especially important as compliance statistics reveal that many employers struggle to meet these requirements, emphasizing the need for awareness among staff. Understanding these regulations empowers career transitioners to negotiate better terms in their new roles, fostering a sense of personal agency during their career journeys.
-
Job Duties Test: The FLSA outlines specific responsibilities that workers must perform to qualify as exempt. Familiarity with these criteria is vital for individuals to accurately assess their classification and rights under the law. For instance, employees engaged in executive, administrative, or professional duties may qualify for exemption, but understanding the nuances of these classifications is key. Those undergoing career transitions should be aware of these classifications to ensure they are not misclassified in their new positions, thus safeguarding their financial interests.
-
Expert Commentary: Labor law experts emphasize the importance of staying informed about changes in minimum salary requirements and overtime regulations. Jessica Looman, a Wage and Hour Administrator, notes, “The Department of Labor is ensuring that lower-paid salaried workers receive their hard-earned pay or get much-deserved time back with their families.” This underscores the ongoing efforts to protect workers’ rights and ensure fair compensation, which is crucial for achieving financial independence.
-
Industry Examples: Different industries may have varying minimum salary requirements based on the nature of the work. For example, the technology sector often has higher salary thresholds compared to retail, reflecting the specialized skills required in these fields. Professionals transitioning careers should consider these differences when exploring new opportunities, as understanding industry standards can enhance their employability and job satisfaction.
By understanding these key aspects of the FLSA, salaried individuals can better navigate their rights and responsibilities, including whether salaried employees can work less than 40 hours per week while ensuring they are compensated fairly and in accordance with the law. Find Your Career 2.0 | Career Ownership Coach Parnell Woodard has assisted hundreds of thousands of individuals in assessing their career possibilities, providing valuable insights into how labor laws impact career transitions. Their unique value proposition lies in offering personalized coaching services that help individuals understand their rights and make informed decisions about their employment status.
Common Misconceptions: Can Salaried Employees Work Less Than 40 Hours?
Many individuals mistakenly believe that salaried employees cannot work less than 40 hours per week. This notion is fraught with misconceptions that can lead to unnecessary stress.
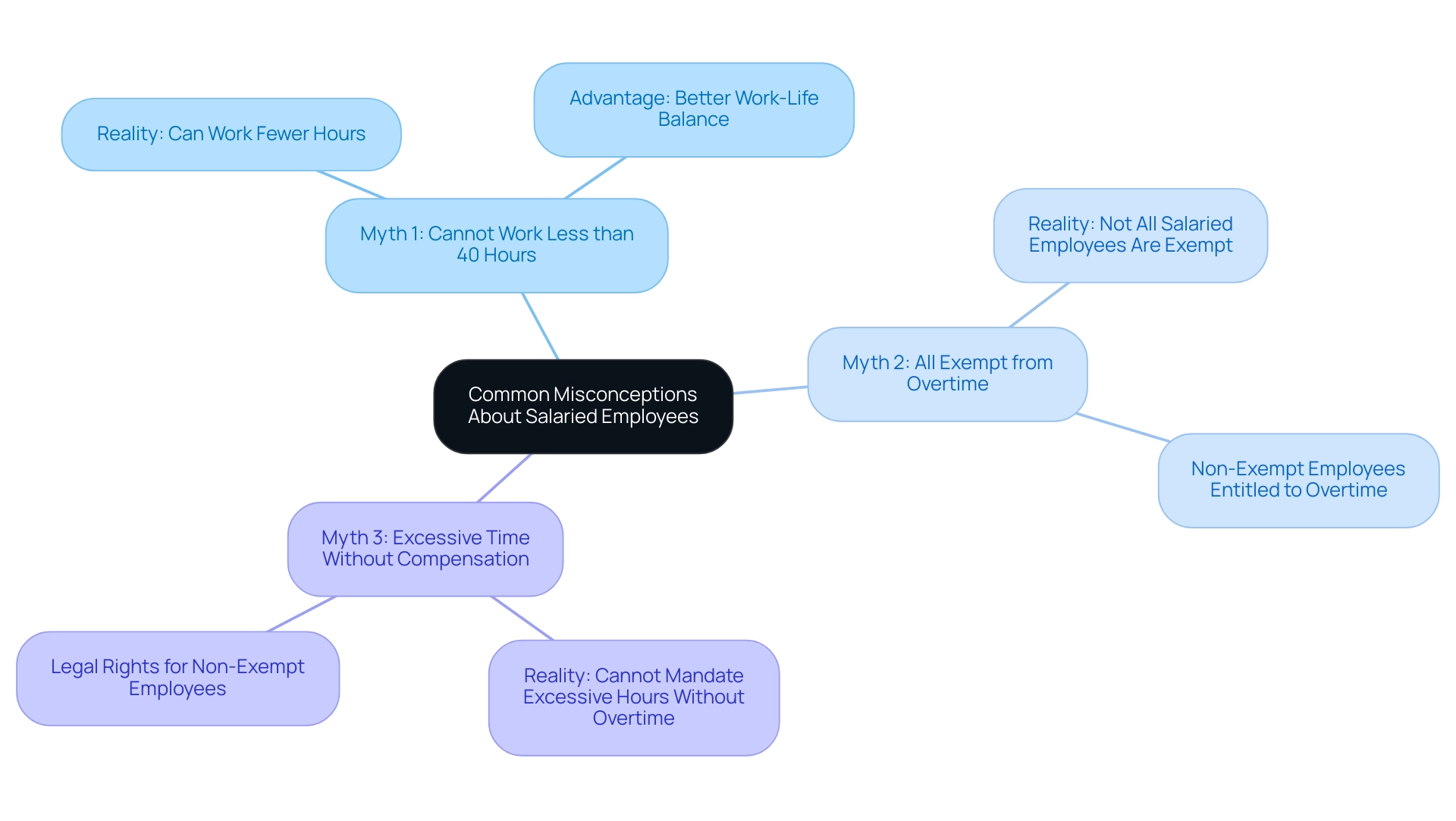
Myth 1: Salaried individuals cannot engage in less than 40 hours.
Reality: Salaried employees can indeed work fewer than 40 hours per week. Their compensation typically remains unchanged unless their employment agreement specifies otherwise. This flexibility can be a significant advantage for those seeking a better work-life balance, especially in a challenging job market where taking charge of one’s professional journey is crucial. The Entrepreneur’s Source has helped countless individuals evaluate their career possibilities, guiding them in making informed decisions and reimagining their professional aspirations.
Myth 2: All salaried workers are exempt from overtime.
Reality: Not all salaried employees are exempt from overtime pay. Only those classified as exempt are not entitled to overtime compensation. Non-exempt salaried staff are entitled to overtime compensation for any time worked beyond the standard 40-hour threshold, ensuring they are rewarded for their extra efforts. It’s essential to understand that deductions from a worker’s predetermined salary can disqualify them from being considered compensated on a ‘salary basis.’ This knowledge is vital for understanding their rights and maintaining financial freedom in their careers.
Myth 3: Employers can mandate salaried staff to put in excessive time without compensation.
Reality: While many employers expect salaried employees to work beyond the typical 40 hours, they cannot legally require non-exempt employees to do so without providing overtime compensation. Understanding this distinction is crucial for workers to defend their rights and ensure fair treatment in the workplace, particularly as they navigate the challenges of a diminishing job market.
Remaining knowledgeable about labor laws and state-specific regulations is critical for compliance and protecting one’s rights as a salaried worker. As Josh Bivens, Director of Research and Policy at the Economic Policy Institute, emphasizes, understanding the legal landscape is vital for employees managing their professional paths. As the employment landscape continues to evolve, awareness of these realities empowers individuals to navigate their careers more effectively and create the lifestyle of their dreams.
The Entrepreneur’s Source provides a thorough and customized approach to coaching, ensuring clients are well-prepared to make informed choices about their professional futures.
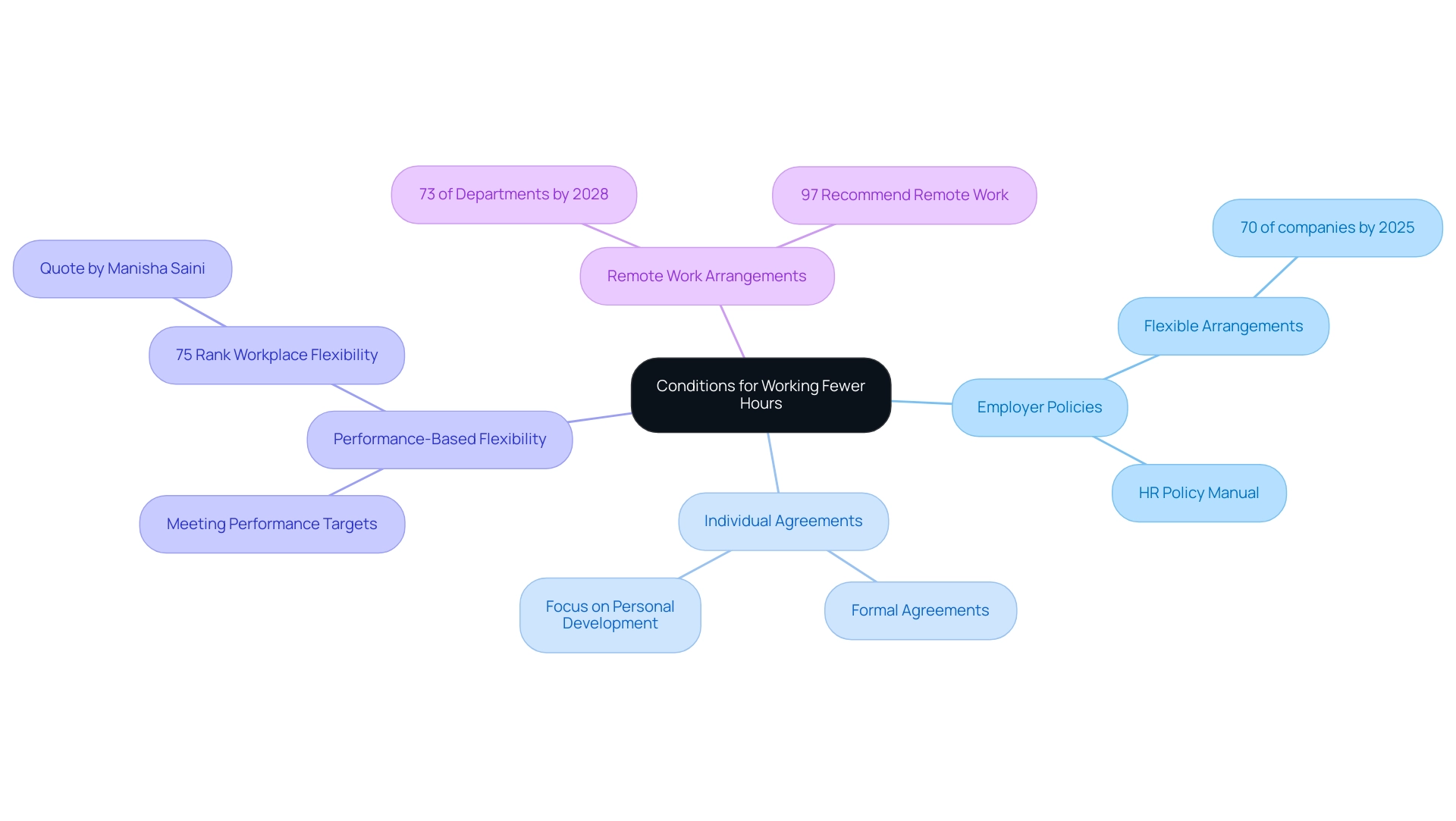
Conditions for Working Fewer Hours: Employer Policies and Agreements
Salaried staff may find opportunities to engage in work that allows them to work less than 40 hours per week under certain conditions. This can significantly enhance their work-life balance and contribute to overall career fulfillment. Here are some key considerations that we believe can help you navigate this journey:
-
Employer Policies: Many organizations are increasingly adopting flexible arrangements that empower personnel to adjust their hours based on workload and personal circumstances. By 2025, around 70% of companies are anticipated to offer some form of flexible arrangements, reflecting a growing trend toward addressing staff needs. This shift is particularly crucial in a challenging job market where traditional career paths may feel limited. We encourage you to refer to your organization’s policy manual or connect with HR to understand the specific provisions available to you.
-
Individual Agreements: Have you considered discussing the possibility of working less than 40 hours per week? This conversation can lead to formal agreements that clearly outline expectations while allowing for reduced hours. Such arrangements can benefit both you and your employer, fostering a more productive professional environment. This flexibility enables you to focus on personal development and financial independence.
-
Performance-Based Flexibility: If you consistently meet or exceed performance targets, you may be in a strong position to request reduced hours without negative repercussions. This performance-driven approach not only highlights your value to the organization but also opens up the possibility of a more adaptable schedule. The question of whether salaried employees can work less than 40 hours per week is increasingly recognized as a significant advantage. According to digital writer Manisha Saini, 75% of staff rank workplace flexibility as their top consideration in job choices.
As remote arrangements continue to gain traction—projected to encompass 73% of all departments by 2028—you should feel empowered to explore these options and advocate for your needs effectively. Moreover, case studies suggest that implementing HR technologies can lead to substantial financial benefits for organizations, such as a small to medium-sized business saving $175,000 in one year. This not only enhances staff satisfaction but also facilitates flexible work arrangements. By understanding your rights and the evolving landscape of employer policies, particularly concerning South Carolina labor laws, you can navigate your career transitions with greater confidence and clarity. Ultimately, this journey is about working towards your desired income, lifestyle, and financial freedom. Remember, you are not alone in this process, and we are here to support you.
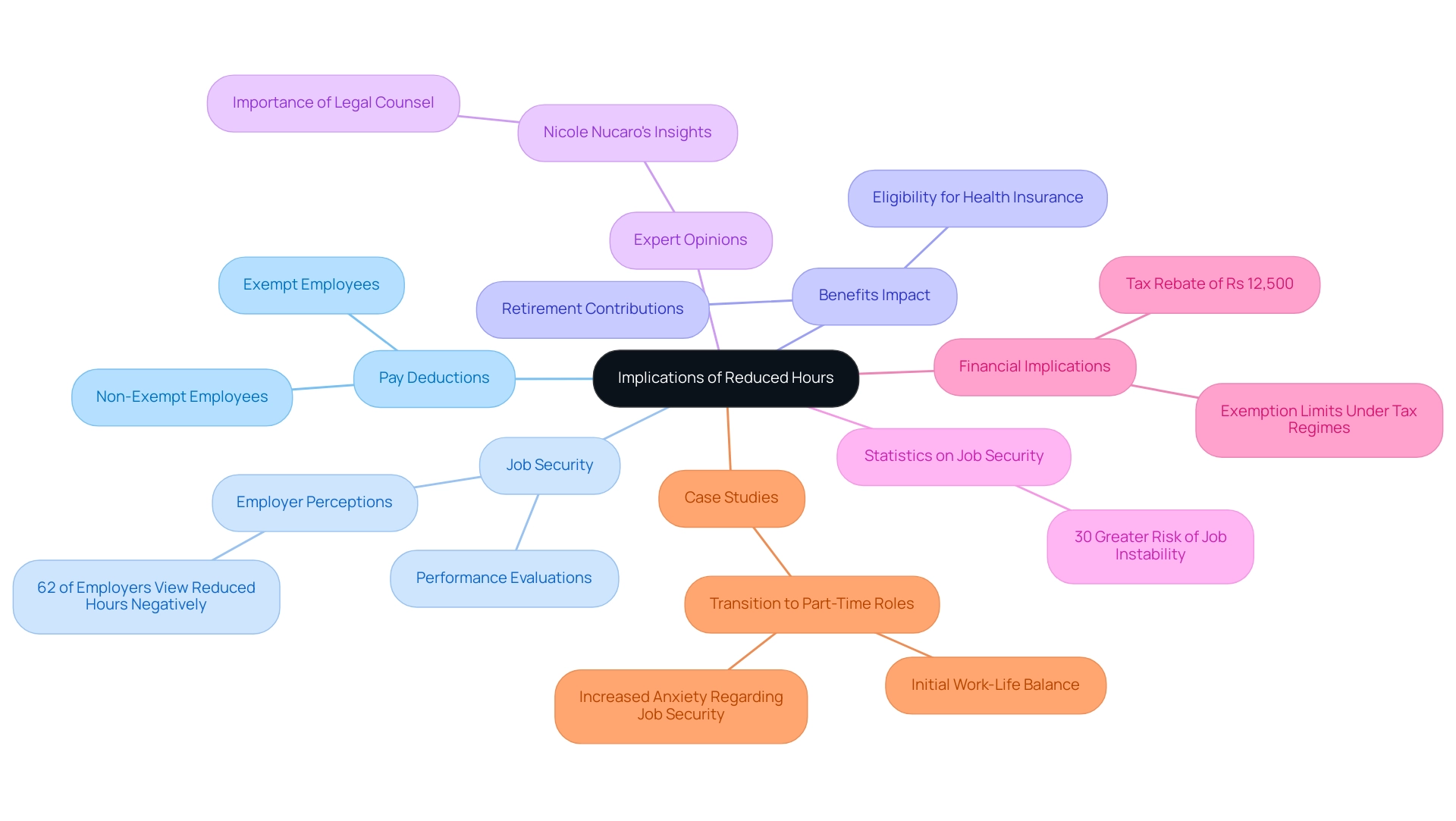
Implications of Reduced Hours: Pay Deductions and Job Security
Working fewer hours as a salaried employee can bring about significant implications that touch on various aspects of employment, and we understand that this can be a challenging situation for many.
-
Pay Deductions: For non-exempt salaried employees, the possibility of pay deductions looms if the agreed-upon hours aren’t met. Employers have the authority to adjust compensation based on actual hours worked, which can feel disheartening. In contrast, exempt staff typically receive their full salary regardless of hours worked. This distinction highlights the importance of understanding one’s classification within the organization, especially in a job market where traditional career paths are narrowing and the value of savings and investments is uncertain.
-
Job Security: Consistently working reduced hours can raise concerns about a worker’s commitment and productivity, which may jeopardize job security. A recent survey revealed that 62% of employers view reduced work schedules as indicative of diminished engagement. This perception can lead to performance evaluations that may not favor the worker. Open communication with supervisors about workload and performance is essential in alleviating these concerns, allowing individuals to demonstrate their ongoing commitment. In a world where job stability can feel fleeting, being proactive about one’s employability is crucial.
-
Benefits Impact: Reduced work hours can also influence eligibility for important benefits, such as health insurance or retirement contributions. Many organizations require employees to work a minimum number of hours to qualify for comprehensive benefits. Understanding company policies regarding benefits is vital for those contemplating a decrease in working hours, as it can significantly impact their overall compensation package. This is particularly pertinent for individuals striving to build wealth and equity in a challenging economic landscape.
-
Expert Opinions: Career experts stress the need for clarity in employment agreements. Nicole Nucaro, an associate in labor law, emphasizes that “working with legal counsel well-versed in these issues is critical to ensure compliance with federal, state, and local requirements, as they are continuously modified.” This underscores the necessity for workers to be aware of their rights and the implications of reduced working hours, especially as they navigate their futures and pursue financial independence.
-
Statistics on Job Security: Current data shows that salaried employees working fewer than 40 hours per week face a 30% greater risk of job instability compared to their full-time counterparts. This statistic highlights the potential risks associated with reduced hours and the importance of proactive career management, particularly in a fluctuating job market.
-
Financial Implications: Additionally, those considering a reduction in working hours should remain mindful of the tax implications. For example, under the previous tax regime, a tax rebate of Rs 12,500 applies to taxable incomes not exceeding Rs 5 lakh, which could influence financial planning for those moving to fewer hours. Understanding how changes in employment status may affect tax planning and benefits is crucial, especially for senior citizens who might have different exemption limits. This financial awareness is essential for anyone aiming to support a longer, active lifestyle.
-
Case Studies: A notable case study involved a group of salaried employees who transitioned to part-time roles. While they initially enjoyed a better work-life balance, many reported increased anxiety regarding job security and benefits eligibility, prompting a reassessment of their career paths. This illustrates the complex relationship between reduced hours and overall job satisfaction, highlighting the need for individuals to explore new opportunities beyond their current circumstances.
In summary, while working reduced hours may present immediate benefits, it is crucial for salaried professionals to reflect on the broader implications regarding compensation, job security, benefits eligibility, and financial planning, particularly in a rapidly changing job market. As emphasized by Find Your Career 2.0 | Career Ownership Coach Parnell Woodard, understanding these factors is essential for navigating career challenges and achieving personal agency in a fluctuating job landscape.
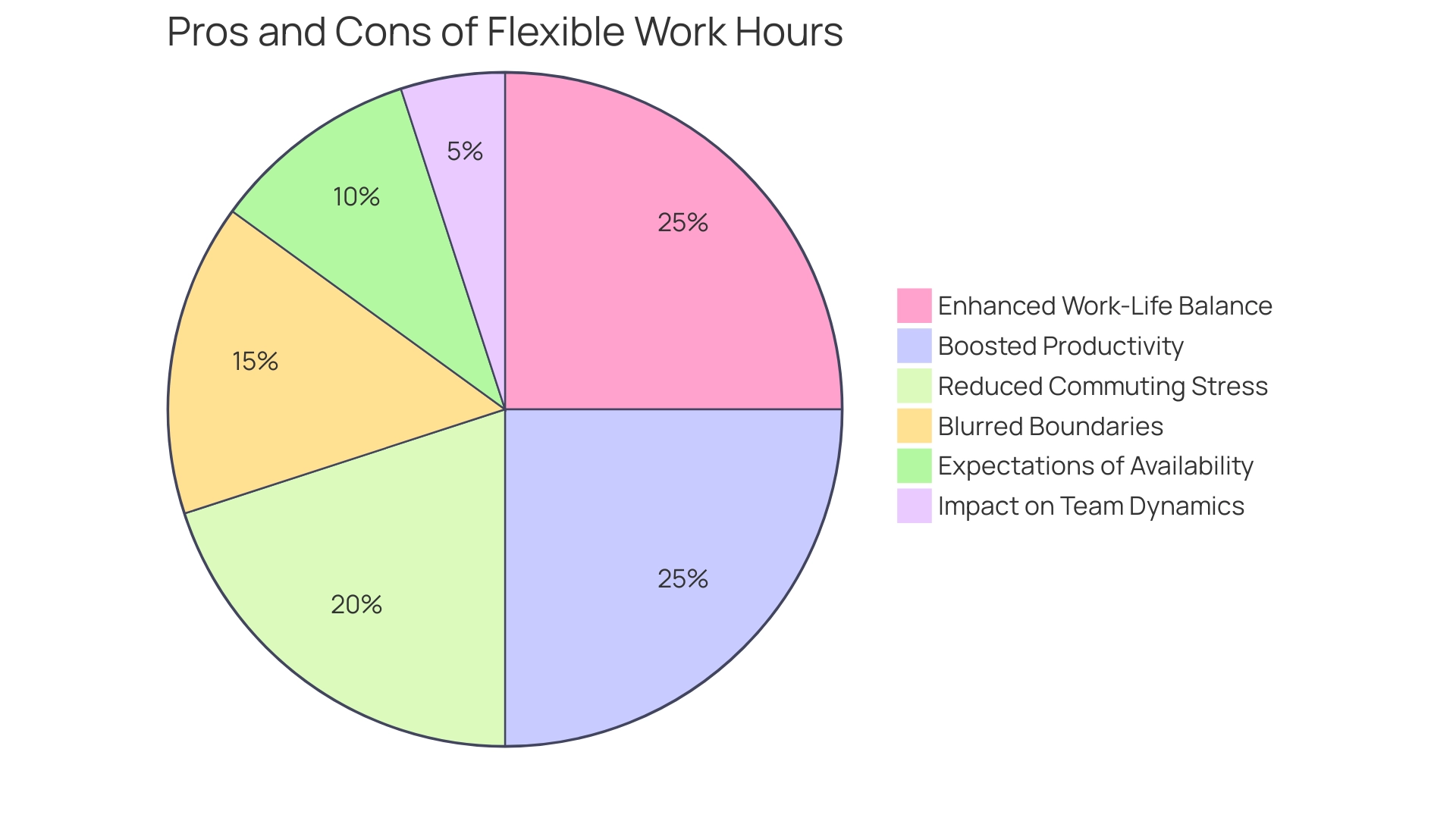
The Pros and Cons of Flexible Work Hours for Salaried Employees
The question of whether salaried employees can work less than 40 hours per week brings to light the various benefits and drawbacks of adaptable schedules for salaried individuals. This topic significantly influences their productivity and overall job satisfaction, and it’s important to explore these dynamics with empathy.
-
Pros:
- Enhanced Work-Life Balance: Flexible hours empower you to align your work schedules with personal commitments, fostering greater job satisfaction. This adaptability is crucial in today’s fast-paced environment, where balancing professional and personal responsibilities is increasingly important. We understand how vital it is to feel fulfilled both at work and at home.
- Boosted Productivity: Many employees report increased productivity when they can choose their working times according to their peak focus periods. In fact, recent statistics indicate that a significant portion of hybrid workers, approximately 58%, engage in practices that enhance their productivity, such as coffee badging, which fosters informal connections and collaboration. Additionally, 90% of remote workers find connecting in the workplace important for their overall happiness, highlighting the role of social interactions in enhancing productivity. You are not alone in seeking a work environment that supports your success.
- Reduced Commuting Stress: Flexibility in hours can alleviate the stress associated with commuting during peak traffic times, positively contributing to your mental well-being and overall job satisfaction. Imagine a work life where your commute doesn’t dictate your mood.
-
Cons:
- Blurred Boundaries: While flexibility offers many benefits, it can also lead to challenges in maintaining a clear separation between work and personal life. This overlap may heighten the risk of burnout, as employees struggle to disconnect from their responsibilities. It’s essential to recognize these risks and find ways to establish boundaries.
- Expectations of Availability: The freedom of flexible schedules can sometimes come with the unspoken expectation of being accessible outside conventional working times. This pressure can diminish the advantages of flexibility, leading to stress and dissatisfaction. Remember, it’s okay to prioritize your well-being.
- Impact on Team Dynamics: Flexible schedules can complicate collaboration and communication within teams. When team members operate on different schedules, it may hinder effective teamwork and project coordination. This highlights the need for clear strategies to maintain cohesion and productivity. The challenges of remote employment underscore the importance of addressing these complexities together.
In summary, while adaptable schedules can significantly improve life balance and productivity, they also introduce challenges that necessitate careful management. As Phyllis Moen observes, “Our research shows that employees who are permitted to have a say in the timing and location of their tasks not only feel better about their positions but also less conflicted about their work-to-family equilibrium.” Crucially, these workers are also more efficient and more productive on the job.
Understanding these dynamics is crucial for salaried individuals considering if they can work less than 40 hours per week with more adaptable arrangements. You deserve a work life that not only meets your professional needs but also nurtures your personal aspirations.
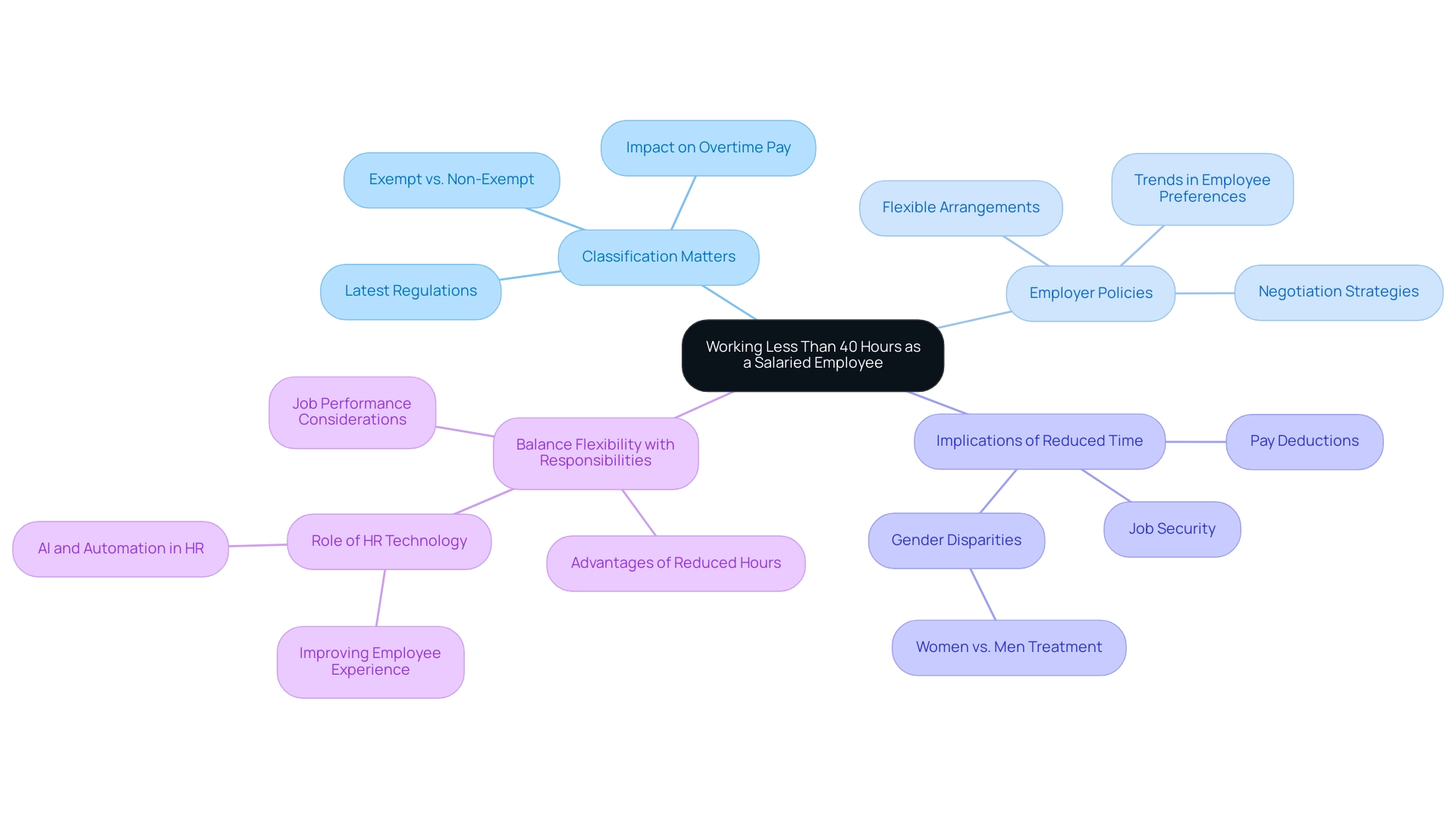
Key Takeaways: Working Less Than 40 Hours as a Salaried Employee
Salaried employees may find themselves with the opportunity to work less than 40 hours per week under specific conditions, but it’s essential to understand the implications involved:
-
Classification Matters: It’s vital to grasp whether you are classified as exempt or non-exempt, as this classification directly influences your rights regarding overtime pay and potential deductions. As we approach 2025, staying informed about the latest employee classification regulations is crucial; these can significantly impact your situation and employability in a challenging job market.
-
Employer Policies: Take the time to familiarize yourself with your company’s guidelines about shifts. Many organizations are becoming more receptive to flexible arrangements. If you desire more flexibility, consider discussing your schedule with your employer. This negotiation can be a pivotal step toward achieving a better work-life balance and financial freedom. Notably, statistics reveal that a considerable number of salaried employees are exploring flexible arrangements, raising the question of whether salaried employees can work less than 40 hours per week, highlighting a growing trend toward prioritizing life balance and personal agency in careers.
-
Implications of Reduced Time: Be aware of the potential consequences of working fewer hours, such as possible pay deductions and impacts on job security. Understanding these implications can empower you to make informed choices about your schedule. As Carolina Aragao pointed out, “Women are significantly more inclined than men (61% vs. 37%) to state a major reason for the gap is that employers treat women differently,” underscoring the importance of recognizing how reduced working time may affect various demographics and their pursuit of employability.
-
Balance Flexibility with Responsibilities: Carefully weigh the advantages and disadvantages of flexible schedules. While reduced hours can enhance your work-life balance, ensuring that your job performance does not suffer is essential. Striking the right balance is key to maintaining both personal satisfaction and professional responsibilities. Additionally, embracing advanced HR technology can aid employees in negotiating flexible hours and improving their life balance, as demonstrated by the case study on HR Technology Trends, which indicates that companies are increasingly adopting AI and automation to enhance HR processes.
As you navigate this landscape in 2025, remember that effective communication with your employer and a clear understanding of your rights can empower you to negotiate a work schedule that aligns with your personal and professional goals. Furthermore, recognizing and leveraging your transferable skills can be crucial in adapting to new roles and opportunities. The Entrepreneur’s Source offers no-cost coaching services and structured processes for career clarity, which can be invaluable as you explore your options and rights in the workplace, ultimately helping you reclaim your career and life goals.
Conclusion
Navigating the intricacies of salaried employment can feel overwhelming, especially in today’s dynamic job market. Understanding the distinction between exempt and non-exempt classifications is essential, as it directly impacts your salary, overtime eligibility, and job security. As the landscape evolves, staying informed about the Fair Labor Standards Act and its implications is crucial for you to secure your rights and financial well-being.
You might wonder if salaried employees can work less than 40 hours per week. Yes, under certain conditions, they can. However, it’s important to be aware of the potential ramifications. Employer policies, individual agreements, and performance-based flexibility all play significant roles in this decision-making process. Additionally, consider the implications of reduced hours, such as pay deductions and job security concerns. These factors must be carefully weighed to maintain your overall career satisfaction.
Ultimately, flexibility in work hours presents both opportunities and challenges. While enhanced work-life balance and increased productivity are compelling advantages, blurred boundaries and expectations of availability can lead to stress and burnout. Striking the right balance is essential for maintaining your job performance while enjoying the benefits of a flexible work arrangement.
As you navigate these complexities, remember that open communication with your employer and a keen understanding of labor laws are paramount. You are not alone in this journey. By empowering yourself with knowledge and leveraging available resources, you can take control of your career path and work towards achieving your personal and professional aspirations. The journey to financial independence and fulfillment is within reach, especially when you are armed with the right information and support.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a salaried position?
A salaried position is one where individuals receive a fixed compensation amount, typically paid monthly or bi-weekly, regardless of the hours they work.
Can salaried employees work less than 40 hours per week?
It depends on their classification. Exempt employees are expected to work the necessary hours to fulfill their responsibilities, often exceeding 40 hours without additional pay. Non-exempt employees can work less than 40 hours and are entitled to overtime pay for hours worked beyond that threshold.
What are exempt employees?
Exempt employees are those who are not entitled to overtime pay and typically hold roles with executive, administrative, or professional responsibilities.
What percentage of salaried workers in the U.S. are classified as exempt?
As of 2025, approximately 65% of salaried workers in the U.S. are categorized as exempt.
What are non-exempt employees?
Non-exempt employees are those who can work less than 40 hours per week and are entitled to overtime compensation at a rate of 1.5 times their regular pay for any hours worked beyond that threshold.
What is the minimum annual salary threshold for non-exempt status as of January 1, 2025?
The minimum annual salary threshold for non-exempt status will rise to $58,656.
How often will salary thresholds update for non-exempt employees?
Starting July 1, 2027, salary thresholds will automatically update every three years.
What are the implications of exempt and non-exempt classifications on workers?
The classification directly impacts workers’ financial well-being and job security, influencing their eligibility for overtime pay and the expectations surrounding their work hours.
What support is available for individuals navigating employment transitions?
Organizations like The Entrepreneur’s Source offer no-cost coaching services and structured processes to help individuals gain clarity and confidence in their career decisions.


